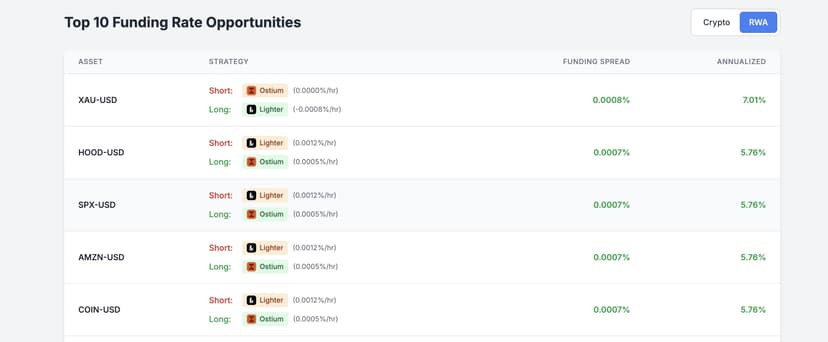
Understanding Onchain Custom Exchanges
A deep dive into onchain custom exchanges like Hyperliquid and BullX, exploring how they work, their advantages, and considerations for traders.

Onchain custom exchanges represent the next generation of decentralized trading platforms, offering sophisticated trading products with the security and transparency benefits of blockchain technology.
What Are Onchain Custom Exchanges?
Onchain custom exchanges are trading platforms built directly on blockchain networks where all transactions, including order placement, matching, and settlement, occur on the blockchain. Unlike centralized exchanges that only use blockchains for deposits and withdrawals, these platforms execute the entire trading process onchain.
Examples of Onchain Custom Exchanges:
- Hyperliquid: A fully onchain perpetual exchange built on a dedicated appchain
- BullX: A Solana-based perpetual futures exchange
- dYdX v4: An orderbook-based derivatives exchange on its own appchain
- GMX: A decentralized spot and perpetual exchange on multiple chains
- Drift Protocol: A Solana-based perpetual futures platform
Key Characteristics of Onchain Exchanges
Transparency
All transactions are visible on the blockchain, including:
- Order execution
- Liquidations
- Fee collection
- Insurance fund operations
Self-Custody
Users maintain control of their assets until the moment of trade execution, reducing counterparty risk associated with centralized exchanges.
Composability
Onchain exchanges can interoperate with other DeFi protocols, enabling:
- Automated trading strategies
- Yield-generating activities with trading positions
- Cross-protocol collateralization
Technical Architecture Models
Onchain exchanges typically use one of several architectural approaches:
1. AMM-Based Systems
Exchanges like GMX use automated market makers with dynamic pricing mechanisms based on:
- Virtual liquidity pools
- Price impact calculations
- External price oracles
2. OrderBook Systems
Platforms like Hyperliquid and dYdX employ onchain orderbooks where:
- Makers post limit orders
- Takers execute against existing orders
- Matching engines run as part of blockchain validation
3. Hybrid Models
Some exchanges combine elements of both approaches:
- AMM for guaranteed liquidity
- Orderbooks for efficient price discovery
- Conditional orders processed by validators
Trading on Onchain Custom Exchanges
Getting Started:
- Set up a compatible crypto wallet
- Deposit funds to the exchange contract or your trading account
- Understand the specific mechanics of the platform you're using
Unique Considerations:
- Gas Costs: Each trade may require gas payments
- Transaction Confirmation Times: Depending on the blockchain, trades may take longer than on centralized alternatives
- MEV Protection: Understanding how the platform handles potential maximal extractable value attacks
Advantages of Onchain Exchanges
Reduced Counterparty Risk
Unlike centralized exchanges, onchain platforms:
- Don't custody user funds (except in smart contracts)
- Can't halt withdrawals during market stress
- Operate transparently with verifiable reserves
Censorship Resistance
Traditional exchanges may:
- Restrict users from certain regions
- Delist assets under regulatory pressure
- Freeze accounts without warning
Onchain exchanges typically offer greater resistance to these issues.
Innovative Trading Features
Many onchain exchanges pioneer new trading mechanisms:
- Cross-margin across multiple positions
- Novel liquidation processes that reduce market impact
- Integration with onchain lending and borrowing
Challenges and Limitations
Performance Constraints
Blockchain throughput limitations can affect:
- Order execution speed
- Maximum orders per second
- Cost efficiency during high volatility
Oracle Dependence
Most platforms rely on price oracles, which:
- Introduce potential points of failure
- May experience delays or inaccuracies
- Could be manipulated in some circumstances
Liquidity Fragmentation
The proliferation of different exchanges across various blockchains has led to:
- Divided liquidity pools
- Varying trading experiences across platforms
- Opportunities for cross-chain arbitrage
The Future of Onchain Exchanges
The onchain exchange ecosystem continues to evolve with:
- Layer 2 solutions improving scalability
- Cross-chain bridges enabling liquidity sharing
- Institutional adoption driving volume growth
- Advanced risk management systems
As blockchain technology advances, these platforms will likely narrow the performance gap with centralized exchanges while maintaining their fundamental security and transparency advantages.
Remember that while onchain exchanges reduce certain risks, they introduce others. Smart contract vulnerabilities, oracle failures, and blockchain congestion can all impact trading on these platforms.